Imagine this: You’ve just undergone a major surgery, a procedure carefully planned and executed. You’re hopeful for a smooth recovery, but in the back of your mind, you can’t shake the fear – what if something goes wrong? What if an infection develops, jeopardizing your healing and potentially causing more complications? This fear is not unfounded, as surgical incisions create a gateway for bacteria and other pathogens, potentially leading to infection. Many factors contribute to this risk, and understanding them is crucial for promoting a safe and successful recovery.

Image: www.vrogue.co
This article delves into the complex world of surgical incision infections, exploring their causes, identifying risk factors, and providing insights into how to mitigate this potential threat. We will also explore strategies for prevention and effective treatment, empowering you with knowledge to navigate this aspect of your health journey with confidence.
Unveiling the Invisible: The Nature of Surgical Incisions and Infection Risk
Surgical incisions are a necessary part of many medical procedures, allowing surgeons access to the body’s internal structures. However, these openings create a breach in the skin, our natural barrier against infection. The skin harbors a complex ecosystem of bacteria, most of which are harmless or even beneficial. But when a surgical incision is introduced, this delicate balance can be disrupted, giving opportunistic pathogens a chance to enter the body.
The risk of infection following surgery is a significant concern for patients and healthcare providers alike. While modern surgical techniques and meticulous infection control measures have greatly reduced this risk, it remains a challenge. An estimated 2–5% of patients undergoing surgery will develop a wound infection, with some procedures carrying even higher risks. Let’s explore the factors that influence this risk.
Risk Factors: Unraveling the Threads of Infection
Numerous factors contribute to the risk of a surgical incision becoming infected. Understanding these factors is crucial for both healthcare professionals making decisions on patient care, and for individuals seeking to understand their own specific risk profiles.
1. The Nature of the Surgery:
The type of surgery plays a crucial role in infection risk. Major surgeries involving complex procedures, longer operating times, and access to contaminated areas, such as the abdomen or bowel, carry a higher infection risk.
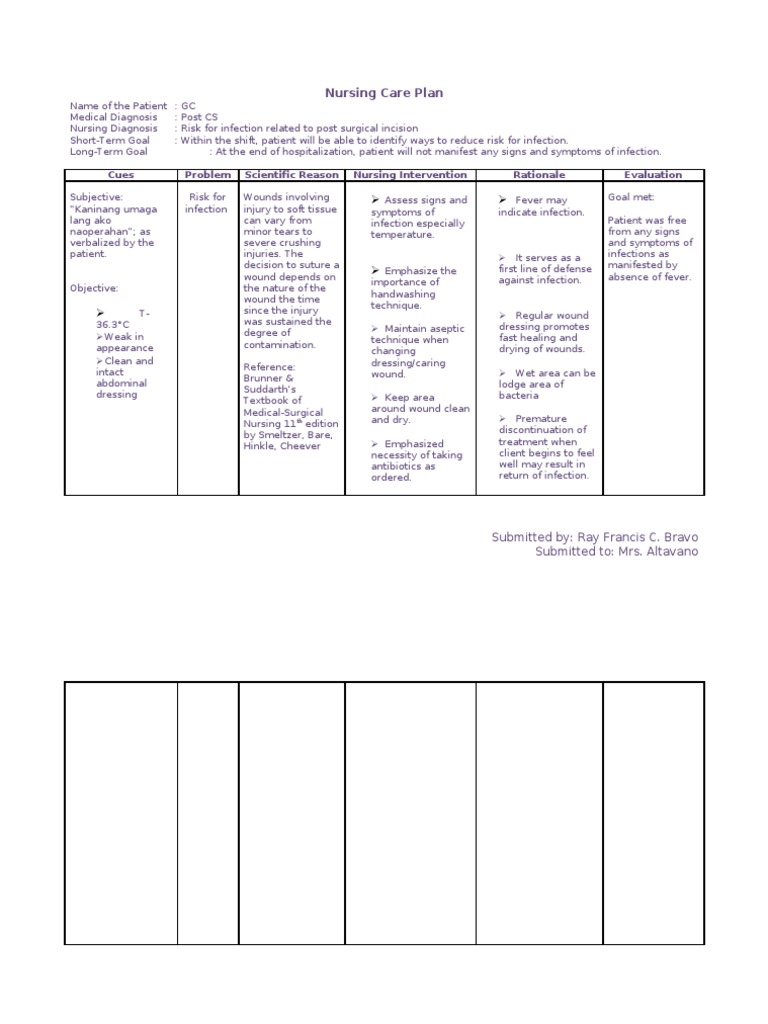
Image: www.scribd.com
2. Patient-Specific Factors:
Some underlying conditions make patients more susceptible to infections. These can include:
- Diabetes: Diabetes compromises the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight off infections.
- Obesity: Obesity can restrict blood flow to tissues, slowing wound healing and increasing infection risk.
- Chronic illnesses: Individuals with chronic diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or heart failure, often have weakened immune systems, making them more vulnerable.
- Immunosuppression: Patients taking immunosuppressant drugs following organ transplantation or for autoimmune diseases have a compromised immune system, rendering them especially susceptible to infection.
3. Pre-Operative Factors:
Conditions prior to the surgery can significantly influence infection risk.
- Poor hygiene: Lack of proper hygiene practices, such as inadequate hand washing, can introduce bacteria into the surgical site.
- Pre-existing skin infections: Having an active skin infection before surgery dramatically increases the risk of wound infection.
- Smoking: Smoking compromises the body’s ability to heal and fight infections, making it a major risk factor.
- Substance abuse: Alcohol and drug abuse can weaken the immune system and impair wound healing.
4. Intra-Operative Factors:
Factors during the surgery itself can also contribute to infection.
- Surgical technique: Using sterile techniques during surgery is essential to minimize the introduction of bacteria into the wound.
- Length of surgery: Longer surgical procedures increase the risk of infection as the wound is exposed to potential contaminants for a longer duration.
- Contamination of the surgical field: Accidental contamination of the surgical site during the procedure can significantly increase the risk of infection.
5. Post-Operative Factors:
Care after surgery is crucial for minimizing infection risk.
- Inadequate wound care: Failure to properly clean and dress the surgical wound can lead to bacteria entering the wound.
- Delayed wound healing: Factors hindering wound healing, such as smoking, poor nutrition, or underlying medical conditions, increase the risk of infection.
- Compromised immune system: Post-operative infections can also stem from weakening of the immune system due to factors such as stress, medications, or underlying illnesses.
Recognizing the Signs: Identifying Surgical Wound Infections
Early identification of surgical wound infections is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing complications. Be aware of these potential signs:
- Redness: Increased redness around the incision site.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the incision.
- Warmth: The area around the incision feels warm to the touch.
- Pain: Increased pain or tenderness around the incision.
- Drainage: Pus or other foul-smelling drainage from the incision.
- Fever: A sudden elevation in body temperature.
Prevention is Power: Strategies for Safe Recovery
While the risk of infection cannot be entirely eliminated, comprehensive preventive measures significantly reduce its likelihood. Here’s what you can do:
-
Pre-operative Preparation:
-
Communicate with your doctor: Be transparent with your doctor about any health conditions, medications, allergies, or concerns you have.
-
Maintain good hygiene: Practice meticulous personal hygiene, including frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially before and after interacting with your incision.
-
Stop smoking: Quitting smoking before surgery is crucial for promoting wound healing and reducing infection risk.
-
Manage underlying conditions: Work with your doctor to manage any existing medical conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, to improve your overall health and minimize infection susceptibility.
-
Intra-operative Precautions:
-
Sterile surgical environment: Ensure your surgeon and the operating room staff maintain strict sterile techniques during the procedure.
-
Minimize surgical time: Discuss with your surgeon any options to minimize the length of the surgery, if possible, to reduce the exposure of the wound to potential contaminants.
-
Post-operative Care:
-
Follow your doctor’s instructions: Adhere carefully to your doctor’s post-operative instructions regarding wound care, medication, diet, and activity limitations.
-
Proper wound cleaning: Keep the incision clean and dry, following your doctor’s guidelines for wound dressing changes.
-
Seek immediate attention: Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any signs of infection.
Empowering Your Recovery: Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
Dr. [Expert Name], a renowned surgeon specializing in infectious disease, underscores the importance of proactive measures: “Patients often underestimate the role they play in their recovery. By taking simple steps like maintaining good hygiene, adhering to wound care instructions, and promptly reporting any unusual symptoms, individuals can make a significant difference in preventing infections.
Dr. [Expert Name] further emphasizes the value of open communication with healthcare professionals: “Don’t hesitate to voice your concerns or questions. A collaborative approach between patient and doctor is crucial for ensuring a smooth and safe recovery.”
Risk For Infection Related To Surgical Incision As Evidenced By
Conclusion: Embracing a Proactive Approach to Wound Healing
Surgical incision infections are a serious concern, but through informed awareness, proactive care, and open communication with your healthcare provider, you can significantly reduce the risk and ensure a successful recovery. Remember, empowering yourself with knowledge gives you the tools to navigate your post-operative journey confidently. Stay informed, practice preventive measures, and prioritize your well-being for a safe and fulfilling recovery.
If you have any further questions or concerns about surgical incision infection, do not hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider. Their expertise and guidance will empower you to make informed decisions regarding your health.






