Imagine a lush green forest, teeming with life. The sun’s rays bathe the leaves, giving them a vibrant glow. This beautiful scene, so full of energy and activity, is powered by two fundamental processes: photosynthesis and respiration. These interconnected processes, the very foundation of life on Earth, are the focus of our journey today. We’ll unravel the intricacies of photosynthesis and respiration, explore the essential concepts, and provide a comprehensive breakdown of the POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) answer key, empowering you to understand these vital processes on a deeper level.

Image: myans.bhantedhammika.net
Photosynthesis and Respiration POGIL activities are commonly used in biology classrooms to enhance understanding and engage students in active learning. These activities take a hands-on approach by letting students work through problems and discover concepts for themselves. This guide will delve into the underlying principles behind these processes, highlighting the beauty and wonder of how life sustains itself.
The Power of the Sun: Photosynthesis – A Symphony of Light and Life
Photosynthesis is a remarkable process, a testament to the ingenious design of the natural world. It’s the very foundation of life on Earth, allowing plants to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugars. This process is a crucial link in the chain that feeds all living organisms.
Let’s break down photosynthesis into its key stages:
1. Capturing Light: Plants use chloroplasts, tiny green organelles within their cells, to capture sunlight. This captivating process begins with a molecule called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy, particularly in the red and blue regions of the spectrum, giving plants their characteristic green color.
2. Light-Dependent Reactions: These reactions, as the name suggests, rely directly on sunlight. The absorbed light energy is used to split water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct – the very air we breathe! In the process, electrons are energized, ready to power the next stage.
3. The Calvin Cycle: This intriguing cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. Here, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is captured and combined with the energized electrons and hydrogen ions (H+) to create glucose, a sugar molecule that provides energy for the plant.
Fueling Life: Respiration – The Engine of Living Organisms
Respiration, a seemingly opposite process to photosynthesis, is essential for living organisms, from bacteria to humans. It’s the intricate breakdown of glucose, releasing the stored chemical energy to power cellular functions and activities.
The key stages of respiration can be summarized as follows:
1. Glycolysis: This initial stage takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glucose is broken down into pyruvate, releasing a small amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells.
2. The Krebs Cycle: Also known as the citric acid cycle, this stage occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell. Pyruvate is further broken down, generating ATP and electron carriers (NADH and FADH2).
3. Electron Transport Chain: This final stage involves a series of protein complexes embedded in the mitochondrial membrane. The energized electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along the chain, releasing energy that is used to pump protons across the membrane. This proton gradient drives ATP synthesis, producing the majority of the cell’s energy.
POGIL Answer Key: Unlocking the Secrets
The process of photosynthesis and respiration is often explored in biology classrooms through POGIL activities, a student-centered approach to learning based on guided inquiry. To assist you in your learning journey, let’s delve into the POGIL answer key, providing a comprehensive breakdown of these essential questions.
Here are some of the common questions you might encounter in a Photosynthesis and Respiration POGIL:
1. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis?
- Reactants: Light energy, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O)
- Products: Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2)
2. What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration?
- Reactants: Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2)
- Products: Carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and energy (ATP)
3. How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related?
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected processes that form a cycle. Photosynthesis captures light energy to produce glucose, which is then used in respiration to release energy for cellular functions. It’s like a delicate balance where the products of one process serve as the reactants for the other.
4. What is the role of ATP in cellular processes?
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the universal energy currency of cells. It stores and releases energy in small, usable packets, powering a wide range of cellular functions, including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and nerve impulse transmission.
5. Describe the structure of a chloroplast and explain its role in photosynthesis.
- Chloroplasts are oval-shaped organelles found in plant cells. They are surrounded by two membranes and contain an internal system of membranes called thylakoids, which are stacked into grana. Chlorophyl is embedded within the thylakoid membranes, capturing light energy and initiating the process of photosynthesis. The stroma, the fluid surrounding the thylakoids, is where the Calvin cycle takes place.
6. Explain the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration.
- Mitochondria are often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell due to their central role in respiration. They are complex organelles with a double membrane, the inner membrane folded into cristae. The electron transport chain, a crucial stage of respiration, takes place within the cristae, generating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
7. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
- Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to break down glucose and produce ATP. It is far more efficient than anaerobic respiration, yielding a much higher amount of energy.
- Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. It is less efficient, producing only a small amount of ATP. In humans, anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid, often leading to muscle fatigue during strenuous exercise.
8. Explain the role of enzymes in photosynthesis and respiration.
- Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They play a crucial role in both photosynthesis and respiration, facilitating specific reactions and ensuring the efficient flow of these processes.
9. Describe how photosynthesis and respiration contribute to the carbon cycle.
- Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and incorporates it into glucose. Respiration releases CO2 back into the atmosphere. This continuous exchange of carbon between organisms and the environment is essential for balancing carbon levels on Earth.
10. How does the process of photosynthesis and respiration impact the environment?
- Photosynthesis is responsible for the oxygen in our atmosphere, making life possible for most organisms. Respiration is a vital process for energy production in all living organisms. These processes are intricately linked to climate change, playing a role in regulating carbon dioxide levels and influencing global temperatures.
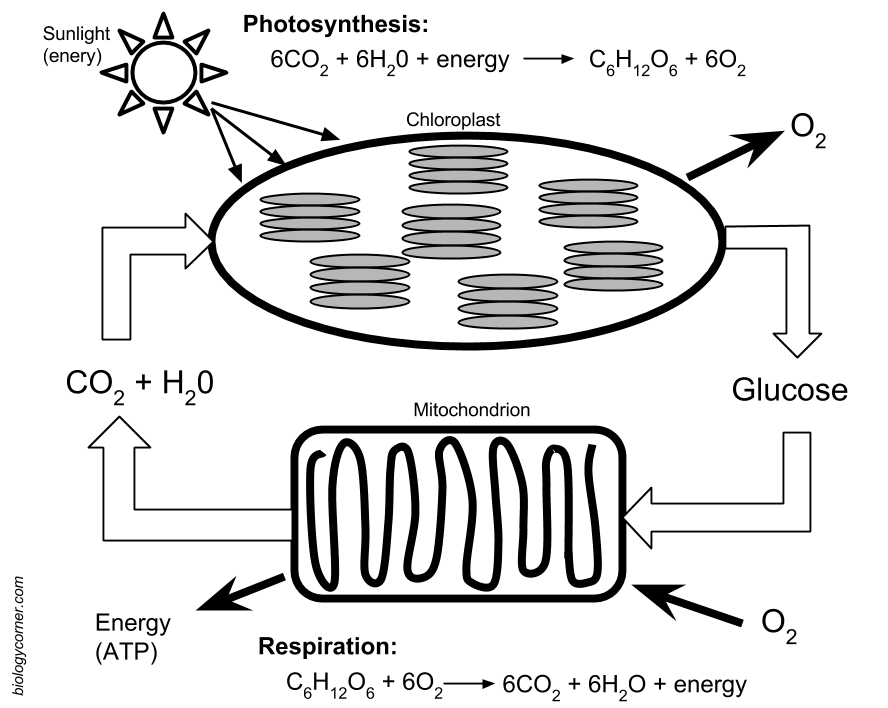
Image: www.biologycorner.com
Expert Insights: Empowering Your Understanding
To further enhance your understanding of photosynthesis and respiration, seek guidance from reputable experts in the field of biology. Consider exploring resources from renowned universities, scientific journals, and online platforms known for their accuracy and credibility.
These resources can provide further insights into the mechanisms of these processes, the latest scientific research, and real-world applications. Remember, the pursuit of knowledge is a lifelong journey, and continuous learning will deepen your understanding of these fundamental concepts.
Photosynthesis And Respiration Pogil Answer Key
Conclusion
Photosynthesis and respiration are the pillars of life, driving energy flow through our planet and enabling all living organisms to thrive. By understanding the intricate mechanisms of these processes, we gain deeper insights into the fascinating tapestry of life on Earth. The POGIL answer key provided in this guide can serve as a valuable tool for your learning journey, deepening your comprehension of these crucial concepts. Continue to explore and investigate, for the world of biology is a boundless realm of discovery and wonder.






