Have you ever wondered what makes up the world around us? Everything from the air we breathe to the chair we sit on, even ourselves, is made up of tiny building blocks called elements. Each element is unique, possessing its own set of properties and characteristics that determine its behavior and role in the universe. One of the key ways we distinguish between elements is by their atomic number and mass. While these numbers might seem abstract, they hold the key to understanding the fundamental nature of matter.

Image: primavse.weebly.com
My fascination with elements started when I was young, mesmerized by the periodic table. The neat rows and columns of symbols, each representing a different element, held a sense of mystery. I wanted to understand what made each element unique. I discovered that one crucial aspect of an element’s identity lies in its atomic number and mass. This journey of exploration led me to the realm of nuclear physics and the secrets hidden within the heart of atoms.
The Foundation of Elements: Atomic Number and Mass
To understand elements, we must first delve into the realm of atoms, the smallest indivisible particles that make up everything. Atoms are composed of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The atomic number of an element refers to the number of protons present in its nucleus. This number is crucial because it signifies the element’s identity. For example, carbon has an atomic number of 6, meaning every carbon atom contains six protons. This number remains constant for a specific element, regardless of the variations in the number of neutrons.
The atomic mass of an element is a bit more complex. It represents the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. While the number of protons determines the element’s identity, the number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element. For instance, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon. Both have six protons, but carbon-12 has six neutrons, while carbon-14 has eight neutrons. The difference in neutron count leads to variations in their atomic mass, and thus their properties.
The Significance of Atomic Numbers and Mass
Atomic numbers and mass play a vital role in shaping our understanding of elements and their behavior. Here’s how:
- Identifying Elements: The atomic number serves as a definitive identifier for each element. It allows us to classify and distinguish different elements on the periodic table. This is crucial for various applications in chemistry, physics, and material science.
- Predicting Chemical Properties: The atomic number, particularly the number of electrons, plays a significant role in determining an element’s chemical properties. The arrangement of electrons in various shells influences how an element interacts with other elements, forming chemical bonds and compounds.
- Understanding Isotopes: Knowing the atomic mass allows us to understand isotopes, variations of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes can have different properties and applications. For instance, carbon-14 is used for radiocarbon dating, while carbon-12 is the most common form of carbon found in nature.
- Nuclear Chemistry and Physics: Atomic numbers and mass are fundamental concepts in nuclear chemistry and physics. They are used to understand nuclear reactions, radioactive decay, and the behavior of atomic nuclei.
- Building Blocks of the Universe: Atomic numbers and mass help us comprehend the composition of the universe, from the lightest element, hydrogen, to the heaviest elements formed in supernovae. This knowledge plays a crucial role in astrophysics and cosmology.
Evolution of Understanding Atomic Numbers and Mass
While the concept of atomic numbers and mass may seem straightforward today, their discovery and understanding have been a long and fascinating journey. Early scientists, like John Dalton, recognized the idea of atoms as fundamental building blocks. However, it was Dmitri Mendeleev who organized elements based on their atomic weight, creating the periodic table, a foundational tool in chemistry. The discovery of the structure of the atom, with its nucleus and electrons, in the early 20th century further refined our understanding of atomic numbers and mass.
The development of advanced techniques like mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy allowed scientists to determine atomic numbers and masses with greater precision. This advancement led to the discovery of isotopes and further paved the way for understanding nuclear processes.
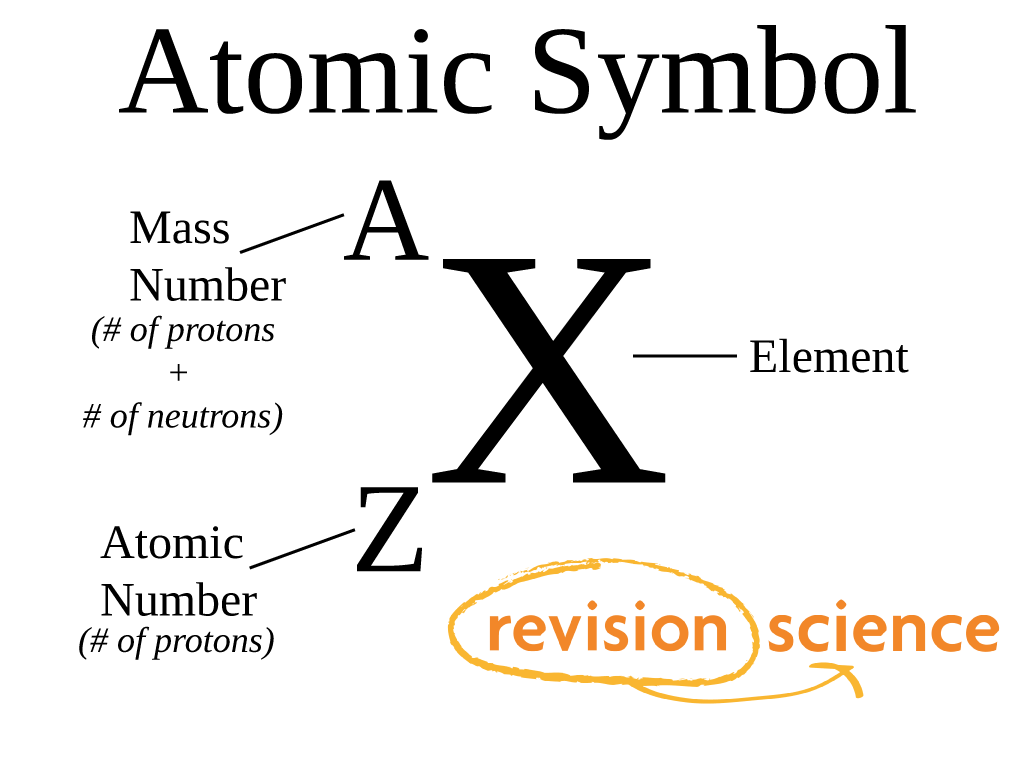
Image: socratic.org
The Future of Atomic Numbers and Mass
Understanding atomic numbers and mass is not just a historical curiosity; it continues to be crucial for ongoing research and development. The study of atomic nuclei and their properties drives innovations in various fields:
- Nuclear Energy: The utilization of nuclear fission and fusion to generate energy relies heavily on an understanding of atomic numbers and mass. It involves manipulating the nuclei of atoms to release vast quantities of energy.
- Medical Isotopes: Radioisotopes with specific atomic masses are used in medical imaging, cancer therapies, and various diagnostic procedures. Their precise properties depend on the number of protons and neutrons in their nucleus.
- Material Science: Scientists are constantly exploring new materials with unique properties, including nano-materials. Understanding the atomic structure, including atomic numbers and mass, allows them to design materials at the atomic level, paving the way for superconductors, advanced catalysts, and materials with unprecedented strength and properties.
Expert Tips for Understanding Atomic Numbers and Mass
Here are some tips that can help you grasp the concepts of atomic numbers and mass:
- Visualize the Atom: Imagine the atom as a tiny solar system with the nucleus as the sun and the electrons orbiting around it like planets. The number of protons in the nucleus represents the element’s identity, and the total number of protons and neutrons gives you the atomic mass.
- Periodic Table as a Guide: The periodic table is your friend. It’s organized based on atomic numbers, providing valuable information about the properties and trends of elements. Use it as a tool to understand relationships between elements and their atomic structures.
- Engage with Examples: Learn through examples. Look up various elements and compare their atomic numbers and atomic masses. Explore isotopes of a specific element and investigate their properties and applications.
- Practice and Research: The more you practice and delve into research related to atomic numbers and mass, the better you will understand these concepts and their importance in various scientific fields.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between atomic number and atomic mass?
A: The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, defining the element’s identity. The atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, which can vary due to the presence of different isotopes.
Q: How do atomic numbers and mass relate to the periodic table?
A: Elements on the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. This organization allows us to predict trends in properties based on the position of elements in the table.
Q: What is the significance of isotopes in scientific research?
A: Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons, leading to variations in their atomic mass and properties. This variation makes them useful for various applications, including radiocarbon dating, medical imaging, and nuclear research.
Q: What are some future advancements expected in the field of atomic numbers and mass?
A: Future advancements are expected in the area of nuclear physics, with a focus on understanding the properties of atomic nuclei and developing new applications for isotopes. Advances in material science and nanotechnology will also involve utilizing the knowledge of atomic numbers and mass to create new materials with unprecedented properties.
Elements With Atomic Number And Mass
https://youtube.com/watch?v=s5iLzhs2zBc
Conclusion
This article has explored the fundamentals of atomic numbers and mass, highlighting their significance in shaping our understanding of elements. We have traced the evolution of our knowledge about these concepts, from early scientists’ observations to modern advancements in nuclear physics, chemistry, and material science. By delving into these fundamental aspects, we gain deeper insights into the composition and behavior of matter, paving the way for exciting discoveries and developments in various scientific fields.
Are you interested in exploring more about atomic numbers and mass? Let us know in the comments below!






