Have you ever found yourself stranded on the side of the road, staring at a dashboard filled with ominous warning lights? Perhaps your headlights have inexplicably gone dark, or your radio has decided to take a permanent vacation. These electrical gremlins can be frustrating, but understanding the heart of your Mercedes E-Class’s electrical system, the fuse box, can be your first step towards a smooth ride. Today, we’re going to demystify this essential component, providing you with the knowledge to navigate its intricate world and potentially save yourself a trip to the mechanic.
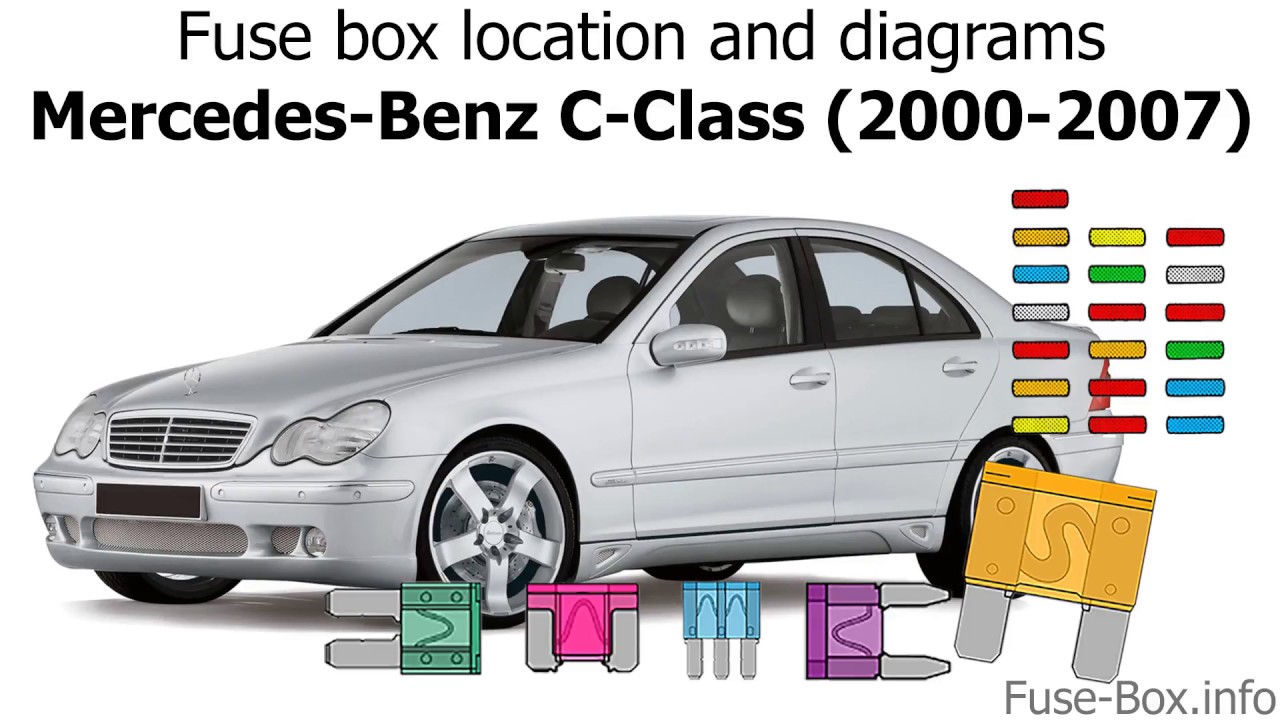
Image: guidelistpalmer.z19.web.core.windows.net
Imagine your car as a complex orchestra, and the fuse box acts as the conductor, orchestrating the flow of electricity to every component. Each fuse acts as a dedicated conductor, safeguarding a specific instrument (or feature!) from being overwhelmed by power surges. By understanding which fuse controls what, you can quickly and easily troubleshoot a wide range of electrical issues. So, if your car’s electrical system is starting to act up, don’t despair! By unraveling the secrets of the Mercedes E-Class fuse box, you’ll be equipped to diagnose and potentially fix these problems yourself.
Locating the Source of Electrical Power: The Fuse Box’s Home
The Mercedes E-Class fuse box is like the central nervous system of your vehicle, housing a network of fuses that protect the electrical components from overheating and potential damage. There are two main fuse boxes in your E-Class:
1. The Engine Compartment Fuse Box
This fuse box is typically located under the hood, near the battery. It is responsible for managing the power to the engine and other vital components like the headlights and cooling system.
2. The Interior Fuse Box
This fuse box is usually found in the driver’s side footwell, beneath the dashboard. It regulates electricity to the interior features such as the radio, windows, and seat controls.
These two fuse boxes work in tandem, ensuring that all of your E-Class’s electrical features are properly powered and protected.
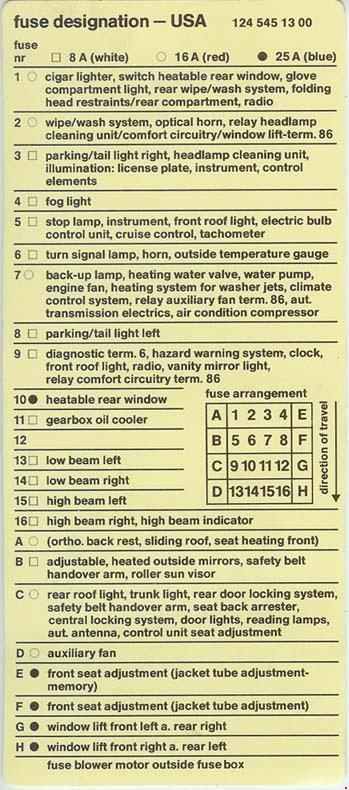
Image: wiremanualhatten.z13.web.core.windows.net
A Deeper Dive: Understanding Fuse Box Diagrams
To understand the fuse box, you’ll need to decode its intricate map – the fuse box diagram. This diagram is basically a blueprint that shows which fuse controls which circuit or feature in your car. This visual guide is crucial for identifying the correct fuse for a particular component when troubleshooting an electrical issue.
Mercedes-Benz has thoughtfully provided these diagrams in their owner’s manuals. If you are using a digital manual, search for keywords like “fuse box,” “fuse diagram,” or “electrical system diagram.” If you have a printed manual, turn to the section covering the electrical system.
The Structure of the Diagram
The fuse box diagram typically consists of the following elements:
- Fuse Panel Layout: A visual representation of the fuse box, showing the location of each fuse.
- Circuit Diagram: A detailed map outlining the wiring of specific circuits, revealing how different parts of your E-Class are connected through the electrical system.
- Fuse Numbering: Each fuse is assigned a specific number, making it easy to identify its location on the diagram.
- Component Labels: The diagram clarifies which circuit or component each fuse is responsible for. For example, you might see a fuse labeled as “Headlights”, indicating that this fuse protects the headlight circuit.
Spotting Trouble: Identifying Fuse Issues
Now that you’ve familiarized yourself with the fuse box diagram, it’s time to sharpen your troubleshooting skills. A blown fuse can manifest in different ways, and being able to identify these signs can be your first step towards a solution:
1. A Component Simply Stops Working
If a feature in your car, like the radio or the headlights suddenly stops working, it’s a strong indication that its corresponding fuse might have blown.
2. Visible Fuse Damage
Closely examine the fuses. If you see a blown fuse, it will appear damaged or melted. A blown fuse generally appears visibly damaged, often with a clear breakage in the center of the fuse.
3. Warning Lights on Your Dashboard
If the fuse box is responsible for the electrical system of a specific feature, a dash warning light associated with that component might illuminate, indicating a potential fuse issue.
Repairing the System: Replacing a Blown Fuse
Once you’ve identified a blown fuse, it’s time to tackle the repair. Replacing a blown fuse is a simple task, but it requires careful attention:
-
Locate the Correct Fuse: Using the fuse box diagram, identify the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component. Pay close attention to the fuse number and its labeled circuit.
-
Turn Off the Ignition: Safety first! Ensure the ignition is switched to the OFF position before attempting any fuse replacement.
-
Pull Out the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to gently remove the blown fuse from its slot.
-
Check the Fuse Rating: Make sure the replacement fuse has the same amperage rating as the original. This information will be printed on the fuse itself or referenced in the fuse box diagram.
-
Insert the New Fuse: Gently insert the new fuse into the empty slot, ensuring that it sits securely.
-
Turn On the Ignition and Test: After replacing the fuse, turn the ignition back on to test if the issue has been resolved. If you still encounter problems, it’s best to consult with a qualified mechanic for further diagnostics.
Expert Tips: Protecting the Fuse Box from Future Blown Fuses
While blowing a fuse is a relatively common issue, there are steps you can take to prevent future mishaps:
-
Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the fuses in your fuse box. Even if a fuse isn’t blown, it may show signs of wear and tear. Replacing these fuses proactively can prevent potential electrical problems down the road.
-
Prevent Overloading: Excessive electrical draw can strain the fuse box. To avoid overload, avoid connecting excessive electrical devices or accessories that draw considerable power.
-
Regular Battery Maintenance: A weak battery can lead to electrical fluctuations that could cause fuse failures. Ensuring your car’s battery is properly serviced and charged can prevent these issues.
A Final Note: When to Consult a Mechanic
While replacing a blown fuse is a simple repair, not every electrical problem is so easily remedied. If you’ve followed the steps above and are still experiencing electrical issues, it’s best to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic has the specialized knowledge and tools to diagnose more complex electrical problems and ensure your car’s electrical system operates smoothly.
Mercedes E Class Fuse Box Location
Conclusion
The Mercedes E-Class fuse box is an often-overlooked, yet vital component responsible for powering the electrical symphony of your car. By understanding the layout of the fuse box, its diagrams, and the common troubleshooting steps, you can navigate the electrical system of your E-Class with a greater sense of confidence. Remember, a blown fuse is usually a simple fix, but a complex electrical problem requires a professional touch. By understanding the fundamentals of your car’s electrical system, you’ll be better equipped to tackle these issues and keep your Mercedes E-Class running smoothly.
This information is provided for educational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional advice. Consult a qualified mechanic for any electrical issues related to your vehicle.






