Ever wondered why your headlights flickered, the radio suddenly went silent, or your power windows ceased to function? The answer could lie in your 2003 Dodge Dakota’s intricate electrical system, specifically the fuse box diagram. Understanding this diagram is crucial for anyone who wants to troubleshoot electrical issues or even just perform basic maintenance. This guide will break down the essentials of your 2003 Dakota’s fuse box diagram, empowering you to conquer those pesky electrical problems.
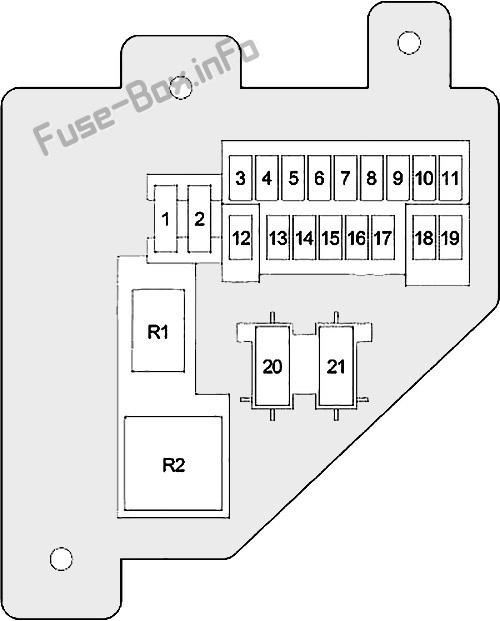
Image: diagramlistgoods.z13.web.core.windows.net
The fuse box diagram is a visual map of your truck’s electrical system, highlighting the fuses and relays that protect various circuits. Fuses act as sacrificial elements, melting to interrupt the flow of electricity before damage can occur to more critical components. Relays, on the other hand, act as switches that control the flow of power to different electrical systems, ensuring efficient operation.
A Deep Dive into the Fuse Box Locations
Your 2003 Dodge Dakota actually features two primary fuse box locations:
1. The Underhood Fuse Box
- Location: Found beneath the hood, close to the battery.
- Purpose: Houses fuses that protect essential components like the engine, lights, and ignition system.
- Diagram: The underhood fuse box diagram is usually found on the inside of the fuse box lid.
2. The Passenger Compartment Fuse Box
- Location: Located on the driver’s side of the dashboard, typically near the lower left corner.
- Purpose: Protects the interior electrical components, such as the radio, power windows, and climate control system.
- Diagram: The passenger compartment fuse box diagram is typically printed on the inside of the fuse box cover.

Image: fixrepairlarson101.z19.web.core.windows.net
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram
The diagrams within your fuse box lids are fairly straightforward, but let’s break down the key elements:
- Fuse Locations: Each fuse is numbered, and the corresponding number is displayed on the diagram, making it easy to locate a specific fuse.
- Circuit Information: The diagram lists the associated circuit for each fuse, using descriptive terms like “headlights,” “power window,” or “radio.”
- Fuse Amperage: Each fuse is rated for a specific amperage, denoted by a number like “10A” or “20A.” This rating indicates the maximum current the fuse can safely handle before melting.
Common Fuse Problems and Troubleshooting
Now that you’re familiar with your fuse box diagram, it’s time to tackle those electrical gremlins. Here’s a breakdown of how to troubleshoot common fuse issues:
-
Identify the Problem: Begin by pinpointing the electrical component that’s malfunctioning. For example, if your headlights aren’t working, you know to focus on the headlight fuses.
-
Locate the Corresponding Fuse: Use the fuse box diagram to determine which fuse protects the malfunctioning circuit.
-
Check the Fuse: Carefully inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will typically appear melted or blackened.
-
Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage. Avoid using higher-amperage fuses, as this can potentially damage electrical components.
-
Test the Circuit: Once you’ve replaced the fuse, turn on the affected system (i.e. the headlights) and see if it’s working.
Beyond the Fuse: When Relays Enter the Picture
While fuses are the first line of defense in your Dakota’s electrical system, relays play a crucial role in controlling the flow of power. Relays are electromechanical switches that use a small electrical current to control a larger current.
Here are some key points about relays:
- Location: Relays are typically found in the underhood fuse box or in a separate relay center.
- Identification: The fuse box diagram will list the specific relays and their associated circuits.
- Troubleshooting: Relays can sometimes fail, causing electrical problems. If you suspect a relay issue, you can test it using a multimeter or simply replace the relay with a new one.
Staying Safe While Tinkering: Electrical Precautions
Working on your car’s electrical system requires caution. Remember these safety tips:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box or any electrical components, always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal.
- Use Insulated Tools: Ensure your tools are insulated to prevent electrical shocks.
- Avoid Wet Conditions: Don’t work on electrical components when it’s raining or the area is wet.
Beyond the Basics: Expanding Your Knowledge
Understanding your 2003 Dodge Dakota’s fuse box diagram is a valuable skill for any owner. It allows you to tackle electrical problems, prevent further damage, and even enhance your truck’s performance. Here are some additional resources to expand your knowledge:
- Online Forums: Find specific forums dedicated to Dodge Dakota owners. You can ask questions, read discussions, and learn from the experiences of others.
- Repair Manuals: Consult your Dakota’s owner’s manual or a repair manual for detailed information on electrical systems, fuse box diagrams, and troubleshooting.
- Professional Assistance: If you encounter a complex electrical issue, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic.
2003 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box Diagram
A Final Word
The fuse box diagram is the key to understanding your 2003 Dodge Dakota’s electrical system. By familiarizing yourself with this diagram and following the troubleshooting steps outlined above, you can confidently tackle minor electrical problems and keep your truck running smoothly. Remember to always exercise caution and prioritize safety when working on your vehicle’s electrical system. Happy troubleshooting!






