Ever had your headlights go out on a dark country road, or your radio suddenly stop working in the middle of a favorite song? You’re not alone. Many 1993 Dodge Dakota owners have experienced these electrical mishaps, and knowing your fuse box layout can be the key to getting back on track. Understanding where each fuse resides and what it controls can save you time, money, and frustration in the long run.
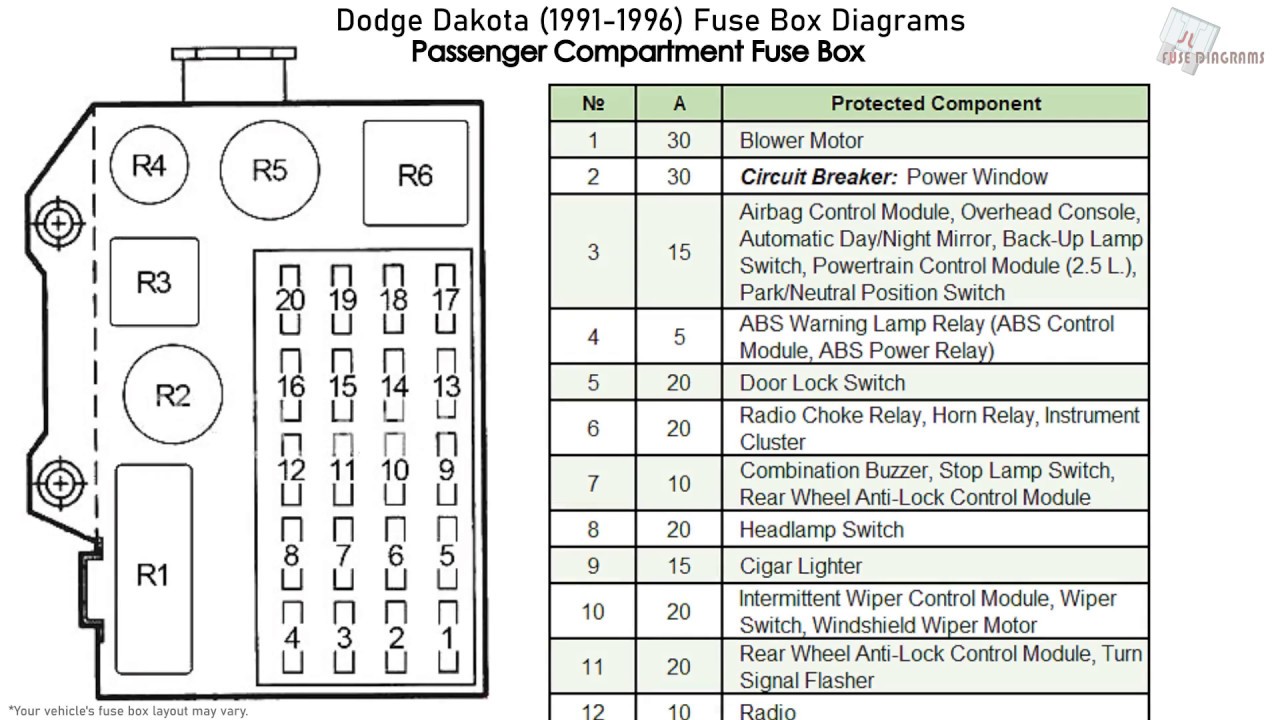
Image: fixenginegottschalk.z19.web.core.windows.net
The fuse box acts as a safety device, protecting your vehicle’s electrical system from overloading. When a fuse blows, it interrupts the flow of electricity to prevent damage to sensitive components. By understanding the layout of your 1993 Dakota’s fuse box, you can quickly identify a blown fuse, replace it, and get back on the road.
Decoding the Fuse Box: A Detailed Look
The 1993 Dodge Dakota has two fuse boxes located under the hood: one on the driver’s side and one on the passenger side. While both are important, the driver’s side fuse box houses the majority of fuses.
Driver’s Side Fuse Box: The Heart of the Electrical System
This is the primary fuse box and holds the bulk of the fuses. The cover itself provides a detailed map, though it can sometimes be faded or difficult to read. Here’s a breakdown of its main sections and common fuse functions:
1. Power Distribution Center (PDC): The Control Center
Located in the center of the driver’s side fuse box, the PDC houses the main relays and fuses responsible for powering essential systems. Here are some key sections within the PDC:
- Fuse Block 1: This group mainly controls interior lighting, gauges, and accessories. Look for fuses relating to the dome light, clock, radio, and cigarette lighter.
- Fuse Block 2: This section primarily handles exterior lighting, such as headlights, brake lights, and turn signals. You’ll find the fuses for the headlights, taillights, and the backup lamp here.
- Fuse Block 3: This block is typically dedicated to power distribution and engine control. Look for the fuses for the ignition system, fuel pump, and engine management system.
![[DIAGRAM] 1993 Dakota Fuse Block Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.2carpros.com/images/question_images/825/original.gif)
Image: mydiagram.online
2. Additional Fuse Locations
Beyond the PDC, you’ll find additional fuses on the driver’s side fuse box cover. These typically control specific accessories or subsystems such as:
- Power Seats: Fuses controlling the motors for electric seats are often found in this area.
- Air Conditioning: The fuse for the air conditioner compressor is usually found here, as well as those for the blower motor and climate control systems.
- Wiper System: Fuses for the windshield wipers, washer system, and rear window defroster are typically housed in this section.
Passenger Side Fuse Box: Supporting the Main System
The passenger side fuse box acts as a complement to the driver’s side box. It primarily contains fuses for accessories, often related to specific trim levels or optional features. Check this fuse box if you’re having problems with your:
- Power Windows: The fuses for the power window motors and switches are usually found here.
- Sunroof: If your Dakota has a sunroof, the fuses controlling its operation will be located in this box.
- Mirror Controls: The fuses managing the power mirrors and heated mirrors are often housed here.
Troubleshooting Tips: Finding the Culprit Fuse
Once you know your way around the fuse box, you can quickly diagnose and fix electrical problems. Follow these steps:
- Identify the Symptom: Decide what’s not working—headlights, radio, power windows, etc. This will help narrow down the possible fuse locations.
- Consult the Fuse Box Diagram: Always refer to the fuse box cover diagram. It provides a detailed list of the fuses and their respective functions.
- Inspect the Fuse: Look for a blown fuse. A blown fuse will be visibly melted or broken.
- Replace the Fuse: Use a replacement fuse with the same amperage rating as the blown fuse. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage, as this could damage your vehicle’s wiring.
- Test the System: Once you’ve replaced the fuse, turn on the system that was malfunctioning to make sure it’s working properly.
- Check for Other Issues: If replacing the fuse doesn’t solve the problem, a more serious electrical fault may exist. You may need to consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis.
Beyond the Fuse Box: Understanding Circuit Breakers
While fuses are common, the 1993 Dodge Dakota also utilizes circuit breakers for specific functions. Circuit breakers are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity automatically when an overload or fault occurs. They are typically resettable, so you can often restore power simply by pressing the reset button.
The most common circuit breaker in the 1993 Dakota is the **Battery Disconnect Switch**, often located under the hood near the battery. This switch is a safety feature designed to completely cut off power to the vehicle for repairs or storage. It also helps prevent battery drain if the vehicle is left idle for extended periods.
Maintaining Your Electrical System: Preventative Steps
While fuse boxes are designed to protect electrical systems, taking preventative measures can further reduce the risk of electrical problems. Some tips for maintaining your Dakota’s electrical system include:
- Regular Fuse Inspection: Check the fuses in both fuse boxes periodically. Look for signs of corrosion, heat damage, or excessive wear.
- Clean the Fuse Box: Keeping the fuse boxes clean and dry can help prevent corrosion and ensure proper contact. Use a soft brush or compressed air to remove debris.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Don’t connect too many accessories or devices to one circuit. This can overload the fuse and cause it to blow.
- Use High-Quality Fuses: Replace blown fuses with genuine Dodge fuses or reputable aftermarket replacements. Using inferior fuses can cause problems down the road.
1993 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box Layout
Conclusion
Knowing your way around the 1993 Dodge Dakota fuse box can be a game changer for anyone who experiences unexpected electrical issues. This guide provides a comprehensive look at the fuse box layout, common fuse functions, and troubleshooting tips. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you can quickly address electrical problems and avoid costly repairs. Remember, regular maintenance and preventative measures are key to keeping your Dakota’s electrical system running smoothly for years to come.






